Currently Empty: ₨ 0
Introduction to fundamental concepts of chemistry
0/18
Atomic Structure
Gases
Liquids
Solids
Chemical Equilibrium
Reaction Kinetics
Thermo-chemistry and Energetics of chemical reactions
Electrochemistry
Chemical bonding
S and p block elements
Transition Elements
Fundamental principles of organic chemistry
Chemistry of Hydrocarbons
Alkyl halides
Alcohols & phenols
Aldehydes and Ketones
Carboxylic acid
Macromolecules
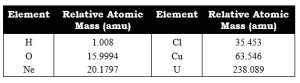
RELATIVE ATOMIC MASS
Relative atomic mass is the mass of an atom of an element as compared to the mass of an atom of carbon taken as 12.
Relative atomic masses are measured in atomic mass units.
1 a.m.u. is 1/12th part of mass of an atom of C-12.
1 a.m.u.= 1.661 x 10-27kg
= 1.661 10-24g
Examples: Na = 23 a.m.u.
Cl = 35.5 a.m.u